Optimizing SEO for Core Web Vitals
Google considers many things when deciding how a webpage will rank and appear in search results. Webpage quality of content is considered along with a few factors Google terms Core Web Vitals.
What Are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals are a category of factors that Google analyzes in order to determine a webpage’s user experience. In other words, these are the factors Google uses to judge a web page’s overall User Experience (UX). UX equates to how people interact with a web page, and it is evaluated by the page’s perceived value, functionality, ease of use, and general impression.
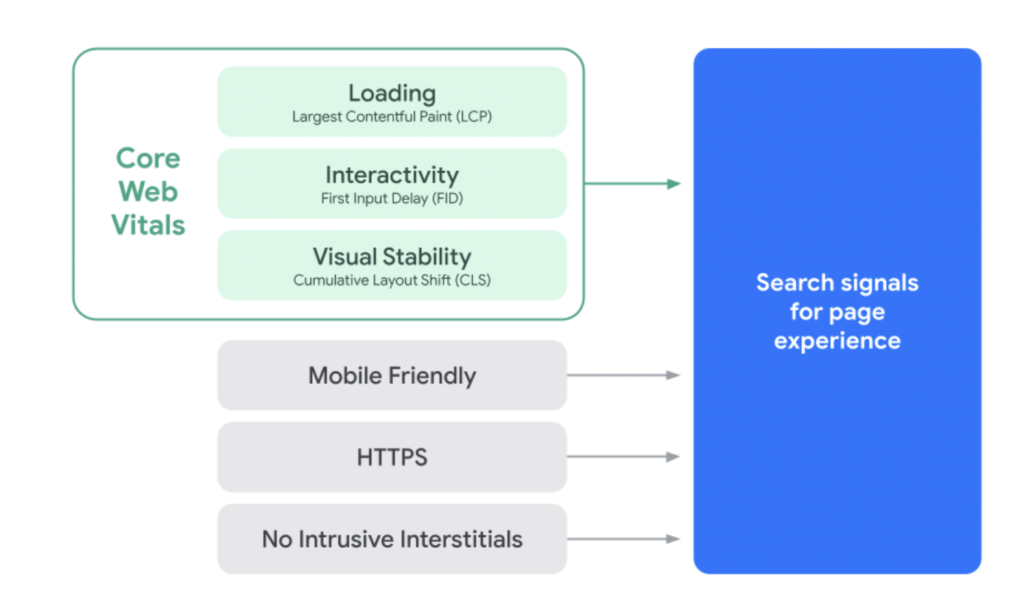
When Google evaluates UX, it takes the following Core Web Vitals into account:
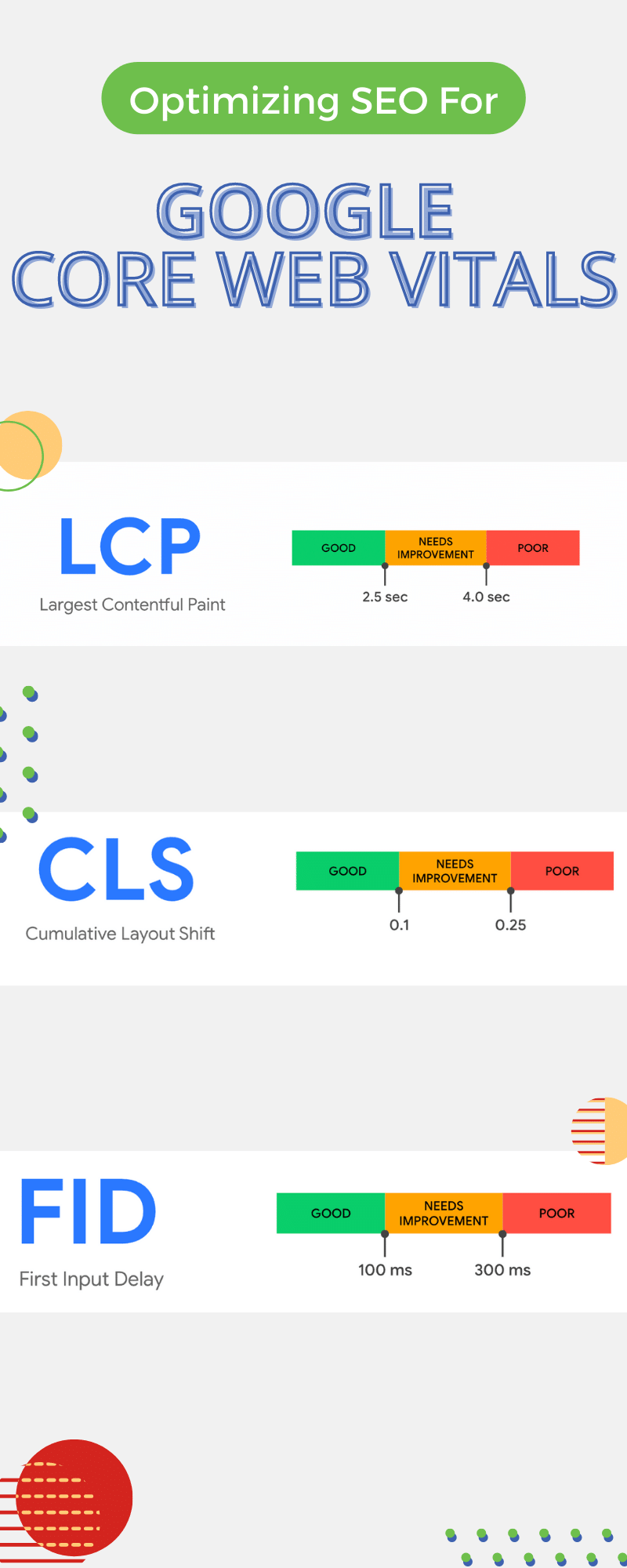
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): A measure of the speed at which the largest image or text block loads.
- First Input Delay (FID): A measure of the speed it takes for the browser to respond when a user engages with the page (i.e. clicks a button).
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): A measure of how stable a webpage appears visually while content elements are loading.
Image provided by Google Search Central
Why Are Core Web Vitals Important?
Google rolled out the Core Web Vitals page experience update on June 15, 2021, to all users globally as an extension to the existing search signals, including mobile-friendliness, HTTPS security, and intrusive interstitial guidelines (features of a webpage that are not accessible to a mobile user).
The search giant announced at the time that tracking Core Web Vitals will be a new way of highlighting great experiences in Google Search:
We believe that providing information about the quality of a web page’s experience can be helpful to users in choosing the search result that they want to visit. On results, the snippet or image preview helps provide topical context for users to know what information a page can provide. At Google Search our mission is to help users find the most relevant and quality sites on the web. The goal with these updates is to highlight the best experiences and ensure that users can find the information they’re looking for.
The goal for many businesses is to create a website that appears in search results–increasing brand awareness, reach, and conversions. Core Web Vitals are important because Google has confirmed that they are a ranking factor in results.
How To Optimize SEO With Core Web Vitals
When it comes to optimizing your website so that it appears in results (known as Search Engine Optimization, or SEO), it’s clear that improving Core Web Vitals will have an impact. Read on for ways to optimize each of the three aspects of Google’s Core Web Vitals to improve SEO.
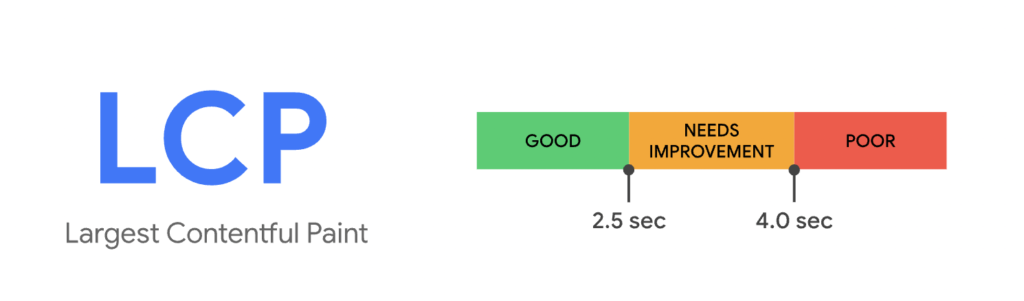
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Google uses LCP measurements to evaluate a web page’s usefulness. Google defines useful in this context as loading enough content that users are able to engage with the webpage.
Largest Contentful Paint replaces performance metrics that Google measured in the past. For example, First Meaningful Paint (FMP) and Speed Index (SI). LCP was chosen as the metric to focus on due to being less complex and hard to explain, as well as more accurate because it measures when the main content of the page has loaded.
What’s A Good LCP?
The goal for optimizing LCP is speed–a fast LCP helps reassure users that the page is working. To optimize the UX and improve SEO, sites should shoot to have an LCP of 2.5 seconds or less. Load time should be measured across mobile and desktop devices to ensure the target is being met for most users.
How to Improve LCP Timing
The following are four factors that can cause a slow LCP:
- Slow server response times
- Render-blocking JavaScript and CSS
- Resource load times
- Client-side rendering
To improve these factors, CSS, fonts, and images should be optimized. Google has specific guides for optimizing each aspect that can affect LCP – see the full list here.
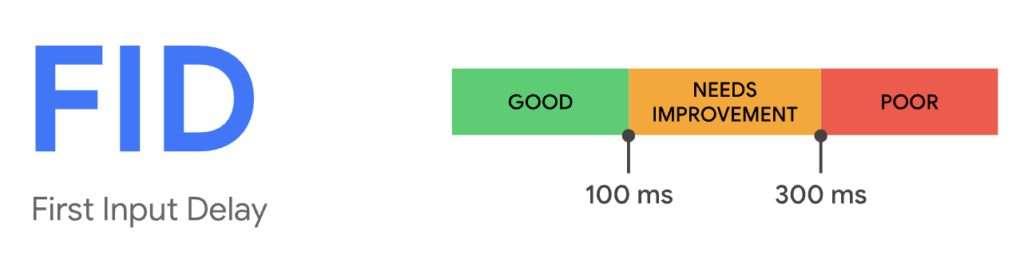
First Input Delay (FID)
Google uses FID to measure the load responsiveness of a webpage or how interactive the page is when the user attempts to use it. Basically, FID is the webpage’s first impression, and a good first impression can lead to lasting relationships (or, in this case, valuable SEO).
While LCP measures how quickly content appears on a screen, FID measures how the site acts when users try to interact with that content. Clicks, taps, and key presses all count as first inputs.
What’s A Good FID Score?
First Input Delay should be measured across mobile and desktop devices to ensure this target is being met for most of the site’s users: an FID of 100 milliseconds or less.
How to Improve FID Score
The following performance techniques can improve a web page’s FID score:
- Reducing the impact of third-party code
- Reducing JavaScript execution time
- Minimizing main thread work
- Keeping request counts low and transfer sizes small
For more detailed instructions on how to improve FID Score, see Google’s optimization recommendations here.
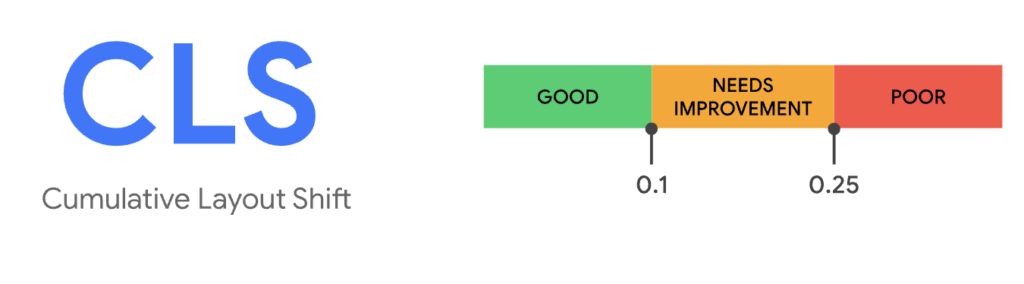
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS measures visual stability, or how users experience unexpected layout shifts. A page that lacks visual stability might have text that moves while you’re reading it, causing you to lose your place. Or a button that disappears right as you’re about to tap on it, causing you to click on an ad instead.
An unstable webpage can be a very annoying experience for users, causing Google to give them a lower ranking. The CLS metric measures how often this annoyance occurs for users.
What’s A Good CLS Score?
Sites should aim to have a CLS score of 0.1 or less. As with the other two metrics, this metric should be analyzed across both mobile and desktop device users.
How to Improve CLS Score
There are a few principles that will ensure all unexpected layout shifts are avoided:
- Images and video elements should have size attributions or have required space reserved with CSS aspect ratio boxes to ensure they have enough space while loading.
- Never insert content above existing content, except in response to a user’s interaction.
- Transitions should only be animated in a way that provides continuity from state to state (i.e. don’t trigger layout changes).
Google outlines how to improve CLS scores in depth here.
Impact of Core Web Vitals on SEO
Core Web Vitals provide just a slice of what Google takes into consideration when deciding a webpage’s ranking by quantifying user experience. Other tips on improving SEO include bettering the site’s overall UX, making changes that improve loading speed, and incorporating content that Google deems valuable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do core web vitals affect SEO?
Core Web Vitals are a great indication of overall site health, which can positively or negatively affect the site's ranking capability. They can improve your website's visiblity and keyword rankings in desktop and mobile web browsers.
Are Google core web vitals important?
Core Web Vitals have become an important metric for determining the quality of a website. A better score indicates users are more likely to stay on the site for longer periods. It's important to measure this data against Google Analytics to ensure stability.
How do Core Web Vitals boost page experience?
There are a number of page speed factors involved in the Core Web Vitals formula to encourage webmasters to improve page experience. Factors like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and First Input Delay (FID) can be given to developers to improve the site overall.